लाल गलियारा
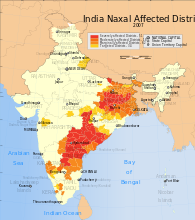
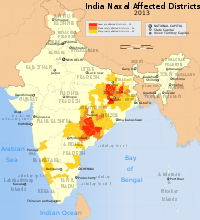
लाल गलियारा भारत के पूर्वी भाग का एक क्षेत्र है जहाँ नक्सलवादी (साम्यवाद) उग्रवादी संगठन सक्रीय हैं।[1] आंध्र प्रदेश, छत्तीसगढ़, उड़ीसा, झारखंड, मध्य प्रदेश, पश्चिम बंगाल और उत्तर प्रदेश के कुछ भागों पर विस्तृत इस क्षेत्र में आधुनिक भारत के सबसे ऊँचे निरक्षरता, निर्धनता और अतिजनसंख्या के दर मिलते हैं।[2][3] भारतीय सरकारी स्रोतों के अनुसार जुलाई २०११ में ८३ ज़िले इस लाल गलियारे में आते थे।[4] फरवरी २०१९ तक, ११ राज्यों के ९० जिले वामपंथी उग्रवाद से प्रभावित हैं।[5]
अर्थव्यवस्था
संपादित करेंलाल गलियारे के क्षेत्रों की अर्थव्यवस्था अक्सर कृषि जैसे प्राथमिक व्यवसायों पर ही टिकी होती है और उसमें विविधता नहीं होती। किसी-किसी इलाक़े में खनिकर्म और वन-सम्पदा से सम्बंधित व्यवसाय भी चलते हैं, लेकिन उद्योग और अन्य विकसित कार्य नहीं हैं। यह अविकसित अर्थव्यवस्था इस क्षेत्र की तेज़ी से बढ़ती आबादी का पोषण करने में अक्षम है।[6][7][8] इसके बावजूद इस क्षेत्र में भारत की प्राकृतिक सम्पदा का एक बड़ा भाग स्थित है, मसलन उड़ीसा में 'भारत का ६०% बॉक्साइट, २५% कोयला, २८% लौह खनिज, ९२% निकल और २८% मैन्गनीज़ स्थित है'।[9]
सन्दर्भ
संपादित करें- ↑ Revelations from the red corridor Archived 2013-01-20 at the वेबैक मशीन, Ajay Agarwal, The Hindustan Times, Accessed 27 अप्रैल 2012
- ↑ Armed revolt in the Red Corridor Archived 2012-07-22 at the वेबैक मशीन, Mondiaal Nieuws, Belgium, Accessed 2008-10-17
- ↑ Women take up guns in India's red corridor Archived 2006-06-22 at the वेबैक मशीन, The Asian Pacific Post, Accessed 2008-10-17
- ↑ "Centre to declare more districts Naxal-hit". मूल से 7 जनवरी 2014 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 11 जनवरी 2013.
- ↑ "Naxal affected Districts". www.pib.gov.in. अभिगमन तिथि 2020-05-15.
- ↑ Fernando Franco, "Pain and Awakening: The Dynamics of Dalit Identity in Bihar, Gujarat and Uttar Pradesh", Indian Social Institute, 2002, ISBN 81-87218-46-0. ... Land deprivation is the major cause of mass poverty especially in view of the low level of economic diversification in rural areas. Amongst all major states, Bihar has the second highest proportion (55 per cent) of landless or quasi-landless households in the rural population ...
- ↑ Dietmar Rothermund, "An Economic History of India: From Pre-colonial Times to 1991", Routledge, 1993, ISBN 0-415-08871-2. Snippet: ... Eastern India has been bypassed by the 'Green revolution' to a great extent ... Instead of urbanization, we can find rural areas with an amazing degree of overpopulation ...
- ↑ Rabindra Nath Pati, National Organization for Family and Population Welfare, "Population, Family, and Culture", Ashish Publishing House, 1987, ISBN 81-7024-151-0.
- ↑ ""Forbes India: industry vs tribals in battleground Orissa", Forbes India Magazine, 03 जुलाई 2009". मूल से 12 अक्तूबर 2012 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 11 जनवरी 2013.