रेडियोसक्रियता
- रेडियोधर्मिता (रेडियोऐक्टिविटी) के अन्य प्रयोगों के लिये रेडियोधर्मिता (बहुविकल्पी) देखें
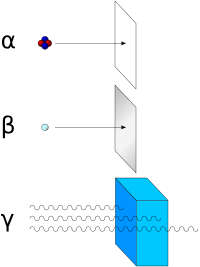
रेडियोसक्रियता (रेडियोऐक्टिविटी / radioactivity) या रेडियोधर्मिता वह प्रकिया होती है जिसमें एक अस्थिर परमाणु अपने नाभिक (न्यूक्लियस) से आयनकारी विकिरण (ionizing radiation) के रूप में ऊर्जा फेंकता है। ऐसे पदार्थ जो स्वयं ही ऐसी ऊर्जा निकालते हों विकिरणशील या रेडियोधर्मी (रेडियोऐक्टिव) कहलाते हैं। यह विकिरण अल्फा कण (alpha particles), बीटा कण (beta particle), गामा किरण (gamma rays) और इलेक्ट्रॉनों के रूप में होती है।[1]
इतिहास
संपादित करेंरेडियोसक्रियता की खोज फ्राँस के वैज्ञानिक हेनरी बेक्वेरल ने 1896 में की थी। यदि यह क्रिया स्वतः होती है, तो इसे प्राकृतिक रेडियो सक्रियता कहते हैं, जबकि मनुष्य के द्वारा करा जाने पर कृत्रिम रेडियो सक्रिता कही जाती है। प्राकृतिक रेडियोसक्रियता मुख्यतः भारी नाभिकों से होती है। यूरेनियम (परमाणु संख्या 92) पहला खोजा गया प्राकृतिक रेडियोसक्रिय तत्व है।[2]
रेडियोसक्रिय समस्थानिकों के उदाहरण
संपादित करेंप्राकृतिक समस्थानिक
संपादित करेंकृत्रिम समस्थानिक
संपादित करेंविभिन्न प्रकार के क्षय
संपादित करेंयद्यपि पहले केवल अल्फा, बीटा और गामा विकिरण की ही खोज हुई थी, किन्तु बाद में पता चला कि कै अन्य प्रकार के उत्सर्जन (emission) भी होते हैं।
| क्षय की प्रणाली | भाग लेने वाले कण | संतति केंद्रक (Daughter nucleus) |
|---|---|---|
| Decays with emission of nucleons: | ||
| अल्फा क्षय | An alpha particle (A = 4, Z = 2) emitted from nucleus | (A − 4, Z − 2) |
| प्रोटॉन उत्सर्जन | A proton ejected from nucleus | (A − 1, Z − 1) |
| न्यूट्रॉन उत्सर्जन | A neutron ejected from nucleus | (A − 1, Z) |
| द्विक प्रोटॉन उत्सर्जन | Two protons ejected from nucleus simultaneously | (A − 2, Z − 2) |
| Spontaneous fission | Nucleus disintegrates into two or more smaller nuclei and other particles | — |
| Cluster decay | Nucleus emits a specific type of smaller nucleus (A1, Z1) which is larger than an alpha particle | (A − A1, Z − Z1) + (A1, Z1) |
| Different modes of beta decay: | ||
| β− decay | A nucleus emits an electron and an electron antineutrino | (A, Z + 1) |
| पॉजिट्रॉन उत्सर्जन (β+ decay) | A nucleus emits a positron and an electron neutrino | (A, Z − 1) |
| Electron capture | A nucleus captures an orbiting electron and emits a neutrino; the daughter nucleus is left in an excited unstable state | (A, Z − 1) |
| Bound state beta decay | A free neutron or nucleus beta decays to electron and antineutrino, but the electron is not emitted, as it is captured into an empty K-shell; the daughter nucleus is left in an excited and unstable state. This process is a minority of free neutron decays (0.0004%) due to the low energy of hydrogen ionization, and is suppressed except in ionized atoms that have K-shell vacancies. | (A, Z + 1) |
| Double beta decay | A nucleus emits two electrons and two antineutrinos | (A, Z + 2) |
| Double electron capture | A nucleus absorbs two orbital electrons and emits two neutrinos – the daughter nucleus is left in an excited and unstable state | (A, Z − 2) |
| Electron capture with positron emission | A nucleus absorbs one orbital electron, emits one positron and two neutrinos | (A, Z − 2) |
| Double positron emission | A nucleus emits two positrons and two neutrinos | (A, Z − 2) |
| Transitions between states of the same nucleus: | ||
| Isomeric transition | Excited nucleus releases a high-energy photon (gamma ray) | (A, Z) |
| Internal conversion | Excited nucleus transfers energy to an orbital electron, which is subsequently ejected from the atom | (A, Z) |
रेडियोसक्रियता से सम्बन्धित खतरे के चिह्न
संपादित करें-
The trefoil symbol used to indicate ionising radiation.
-
2007 ISO radioactivity danger symbol intended for IAEA Category 1, 2 and 3 sources defined as dangerous sources capable of death or serious injury.[3]
-
The dangerous goods transport classification sign for radioactive materials
रेडियोसक्रिय तत्व
संपादित करेंइन्हें भी देखें
संपादित करें- विकिरण सुरक्षा (radiation protection)
- आयनकारी विकिरण (ionizing radiation)
- अर्धायु काल (half life period)
सन्दर्भ
संपादित करें- ↑ Stabin, Michael G. (2007). "3". Radiation Protection and Dosimetry: An Introduction to Health Physics. Springer. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-49983-3. ISBN 978-0387499826.
- ↑ "रेडियोसक्रियता आलोक पाण्डेय द्वारा". मूल से 4 अप्रैल 2019 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 30 सितंबर 2016.
- ↑ "IAEA news release Feb 2007". मूल से 17 फ़रवरी 2007 को पुरालेखित. अभिगमन तिथि 30 सितंबर 2016.